MemoryStore¶
MemoryStore manages blocks of data in memory for BlockManager.
Creating Instance¶
MemoryStore takes the following to be created:
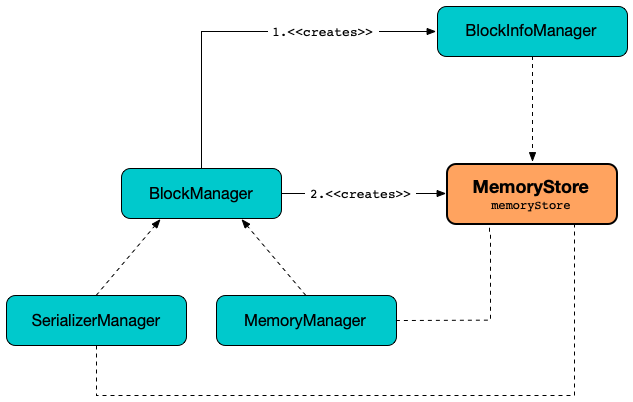
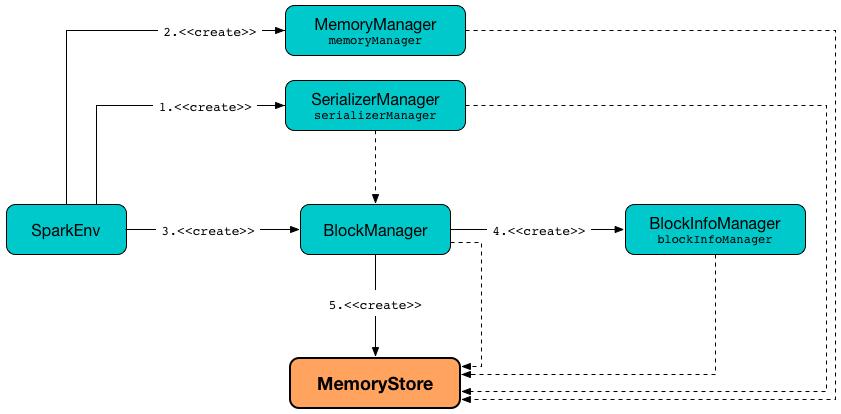
MemoryStore is created when:
BlockManageris created
Blocks¶
entries: LinkedHashMap[BlockId, MemoryEntry[_]]
MemoryStore creates a LinkedHashMap (Java) of blocks (as MemoryEntries per BlockId) when created.
entries uses access-order ordering mode where the order of iteration is the order in which the entries were last accessed (from least-recently accessed to most-recently). That gives LRU cache behaviour when MemoryStore is requested to evict blocks.
MemoryEntries are added in putBytes and putIterator.
MemoryEntries are removed in remove, clear, and while evicting blocks to free up memory.
DeserializedMemoryEntry¶
DeserializedMemoryEntry is a MemoryEntry for block values with the following:
Array[T](for the values)sizeON_HEAPmemory mode
SerializedMemoryEntry¶
SerializedMemoryEntry is a MemoryEntry for block bytes with the following:
ChunkedByteBuffer(for the serialized values)sizeMemoryMode
spark.storage.unrollMemoryThreshold¶
MemoryStore uses spark.storage.unrollMemoryThreshold configuration property when requested for the following:
Evicting Blocks¶
evictBlocksToFreeSpace(
blockId: Option[BlockId],
space: Long,
memoryMode: MemoryMode): Long
evictBlocksToFreeSpace finds blocks to evict in the entries registry (based on least-recently accessed order and until the required space to free up is met or there are no more blocks).
Once done, evictBlocksToFreeSpace returns the memory freed up.
When there is enough blocks to drop to free up memory, evictBlocksToFreeSpace prints out the following INFO message to the logs:
[n] blocks selected for dropping ([freedMemory]) bytes)
evictBlocksToFreeSpace drops the blocks one by one.
evictBlocksToFreeSpace prints out the following INFO message to the logs:
After dropping [n] blocks, free memory is [memory]
When there is not enough blocks to drop to make room for the given block (if any), evictBlocksToFreeSpace prints out the following INFO message to the logs:
Will not store [blockId]
evictBlocksToFreeSpace is used when:
StorageMemoryPoolis requested to acquire memory and free up space to shrink pool
Dropping Block¶
dropBlock[T](
blockId: BlockId,
entry: MemoryEntry[T]): Unit
dropBlock requests the BlockEvictionHandler to drop the block from memory.
If the block is no longer available in any other store, dropBlock requests the BlockInfoManager to remove the block (info).
BlockInfoManager¶
MemoryStore is given a BlockInfoManager when created.
MemoryStore uses the BlockInfoManager when requested to evict blocks.
Accessing MemoryStore¶
MemoryStore is available to other Spark services using BlockManager.memoryStore.
import org.apache.spark.SparkEnv
SparkEnv.get.blockManager.memoryStore
Serialized Block Bytes¶
getBytes(
blockId: BlockId): Option[ChunkedByteBuffer]
getBytes returns the bytes of the SerializedMemoryEntry of a block (if found in the entries registry).
getBytes is used (for blocks with a serialized and in-memory storage level) when:
BlockManageris requested for the serialized bytes of a block (from a local block manager), getLocalValues, maybeCacheDiskBytesInMemory
Fetching Deserialized Block Values¶
getValues(
blockId: BlockId): Option[Iterator[_]]
getValues returns the values of the DeserializedMemoryEntry of the given block (if available in the entries registry).
getValues is used (for blocks with a deserialized and in-memory storage level) when:
BlockManageris requested for the serialized bytes of a block (from a local block manager), getLocalValues, maybeCacheDiskBytesInMemory
putIteratorAsBytes¶
putIteratorAsBytes[T](
blockId: BlockId,
values: Iterator[T],
classTag: ClassTag[T],
memoryMode: MemoryMode): Either[PartiallySerializedBlock[T], Long]
putIteratorAsBytes requires that the block is not already stored.
putIteratorAsBytes putIterator (with the given BlockId, the values, the MemoryMode and a new SerializedValuesHolder).
If successful, putIteratorAsBytes returns the estimated size of the block. Otherwise, a PartiallySerializedBlock.
putIteratorAsBytes prints out the following WARN message to the logs when the initial memory threshold is too large:
Initial memory threshold of [initialMemoryThreshold] is too large to be set as chunk size.
Chunk size has been capped to "MAX_ROUNDED_ARRAY_LENGTH"
putIteratorAsBytes is used when:
BlockManageris requested to doPutIterator (for a block with StorageLevel with useMemory and serialized)
putIteratorAsValues¶
putIteratorAsValues[T](
blockId: BlockId,
values: Iterator[T],
memoryMode: MemoryMode,
classTag: ClassTag[T]): Either[PartiallyUnrolledIterator[T], Long]
putIteratorAsValues putIterator (with the given BlockId, the values, the MemoryMode and a new DeserializedValuesHolder).
If successful, putIteratorAsValues returns the estimated size of the block. Otherwise, a PartiallyUnrolledIterator.
putIteratorAsValues is used when:
BlockStoreUpdateris requested to saveDeserializedValuesToMemoryStoreBlockManageris requested to doPutIterator and maybeCacheDiskValuesInMemory
putIterator¶
putIterator[T](
blockId: BlockId,
values: Iterator[T],
classTag: ClassTag[T],
memoryMode: MemoryMode,
valuesHolder: ValuesHolder[T]): Either[Long, Long]
putIterator returns the (estimated) size of the block (as Right) or the unrollMemoryUsedByThisBlock (as Left).
putIterator requires that the block is not already in the MemoryStore.
putIterator reserveUnrollMemoryForThisTask (with the spark.storage.unrollMemoryThreshold for the initial memory threshold).
If putIterator did not manage to reserve the memory for unrolling (computing block in memory), it prints out the following WARN message to the logs:
Failed to reserve initial memory threshold of [initialMemoryThreshold]
for computing block [blockId] in memory.
putIterator requests the ValuesHolder to storeValue for every value in the given values iterator. putIterator checks memory usage regularly (whether it may have exceeded the threshold) and reserveUnrollMemoryForThisTask when needed.
putIterator requests the ValuesHolder for a MemoryEntryBuilder (getBuilder) that in turn is requested to build a MemoryEntry.
putIterator releaseUnrollMemoryForThisTask.
putIterator requests the MemoryManager to acquireStorageMemory and stores the block (in the entries registry).
In the end, putIterator prints out the following INFO message to the logs:
Block [blockId] stored as values in memory (estimated size [size], free [free])
In case of putIterator not having enough memory to store the block, putIterator logUnrollFailureMessage and returns the unrollMemoryUsedByThisBlock.
putIterator is used when:
MemoryStoreis requested to putIteratorAsValues and putIteratorAsBytes
logUnrollFailureMessage¶
logUnrollFailureMessage(
blockId: BlockId,
finalVectorSize: Long): Unit
logUnrollFailureMessage prints out the following WARN message to the logs and logMemoryUsage.
Not enough space to cache [blockId] in memory! (computed [size] so far)
logMemoryUsage¶
logMemoryUsage(): Unit
logMemoryUsage prints out the following INFO message to the logs (with the blocksMemoryUsed, currentUnrollMemory, numTasksUnrolling, memoryUsed, and maxMemory):
Memory use = [blocksMemoryUsed] (blocks) + [currentUnrollMemory]
(scratch space shared across [numTasksUnrolling] tasks(s)) = [memoryUsed].
Storage limit = [maxMemory].
Storing Block¶
putBytes[T: ClassTag](
blockId: BlockId,
size: Long,
memoryMode: MemoryMode,
_bytes: () => ChunkedByteBuffer): Boolean
putBytes returns true only after there was enough memory to store the block (BlockId) in entries registry.
putBytes asserts that the block is not stored yet.
putBytes requests the MemoryManager for memory (to store the block) and, when successful, adds the block to the entries registry (as a SerializedMemoryEntry with the _bytes and the MemoryMode).
In the end, putBytes prints out the following INFO message to the logs:
Block [blockId] stored as bytes in memory (estimated size [size], free [size])
putBytes is used when:
BlockStoreUpdateris requested to save serialized values (to MemoryStore)BlockManageris requested to maybeCacheDiskBytesInMemory
Memory Used for Caching Blocks¶
blocksMemoryUsed: Long
blocksMemoryUsed is the total memory used without (minus) the memory used for unrolling.
blocksMemoryUsed is used for logging purposes (when MemoryStore is requested to putBytes, putIterator, remove, evictBlocksToFreeSpace and logMemoryUsage).
Total Storage Memory in Use¶
memoryUsed: Long
memoryUsed requests the MemoryManager for the total storage memory.
memoryUsed is used when:
MemoryStoreis requested for blocksMemoryUsed and to logMemoryUsage
Maximum Storage Memory¶
maxMemory: Long
maxMemory is the total amount of memory available for storage (in bytes) and is the sum of the maxOnHeapStorageMemory and maxOffHeapStorageMemory of the MemoryManager.
Tip
Enable INFO logging for MemoryStore to print out the maxMemory to the logs when created:
MemoryStore started with capacity [maxMemory] MB
maxMemory is used when:
MemoryStoreis requested for the blocksMemoryUsed and to logMemoryUsage
Dropping Block from Memory¶
remove(
blockId: BlockId): Boolean
remove returns true when the given block (BlockId) was (found and) removed from the entries registry successfully and the memory released (from the MemoryManager).
remove removes (drops) the block (BlockId) from the entries registry.
If found and removed, remove requests the MemoryManager to releaseStorageMemory and prints out the following DEBUG message to the logs (with the maxMemory and blocksMemoryUsed):
Block [blockId] of size [size] dropped from memory (free [memory])
remove is used when:
BlockManageris requested to dropFromMemory and removeBlockInternal
Releasing Unroll Memory for Task¶
releaseUnrollMemoryForThisTask(
memoryMode: MemoryMode,
memory: Long = Long.MaxValue): Unit
releaseUnrollMemoryForThisTask finds the task attempt ID of the current task.
releaseUnrollMemoryForThisTask uses the onHeapUnrollMemoryMap or offHeapUnrollMemoryMap based on the given MemoryMode.
(Only when the unroll memory map contains the task attempt ID) releaseUnrollMemoryForThisTask descreases the memory registered in the unroll memory map by the given memory amount and requests the MemoryManager to releaseUnrollMemory. In the end, releaseUnrollMemoryForThisTask removes the task attempt ID (entry) from the unroll memory map if the memory used is 0.
releaseUnrollMemoryForThisTask is used when:
Taskis requested to run (and is about to finish)MemoryStoreis requested to putIteratorPartiallyUnrolledIteratoris requested toreleaseUnrollMemoryPartiallySerializedBlockis requested todiscardandfinishWritingToStream
Logging¶
Enable ALL logging level for org.apache.spark.storage.memory.MemoryStore logger to see what happens inside.
Add the following line to conf/log4j.properties:
log4j.logger.org.apache.spark.storage.memory.MemoryStore=ALL
Refer to Logging.