TaskMemoryManager¶
TaskMemoryManager manages the memory allocated to a single task (using MemoryManager).
TaskMemoryManager assumes that:
- The number of bits to address pages is
13 - The number of bits to encode offsets in pages is
51(64 bits - 13 bits) - Number of pages in the page table and to be allocated is
8192(1 <<13) - The maximum page size is
15GB(((1L << 31) - 1) * 8L)
Creating Instance¶
TaskMemoryManager takes the following to be created:
- MemoryManager
- Task Attempt ID
TaskMemoryManager is created when:
TaskRunneris requested to run
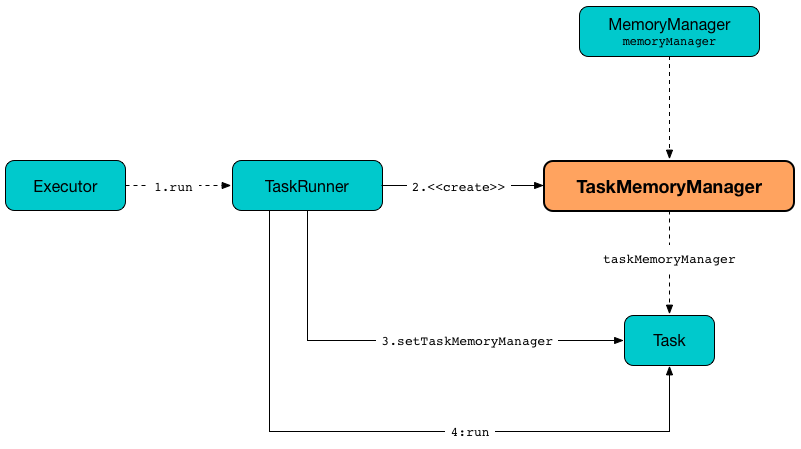
MemoryManager¶
TaskMemoryManager is given a MemoryManager when created.
TaskMemoryManager uses the MemoryManager when requested for the following:
- Acquiring, releasing or cleaning up execution memory
- Report memory usage
- pageSizeBytes
- Allocating a memory block for Tungsten consumers
- freePage
- getMemoryConsumptionForThisTask
Page Table (MemoryBlocks)¶
TaskMemoryManager uses an array of MemoryBlocks (to mimic an operating system's page table).
The page table uses 13 bits for addressing pages.
A page is "stored" in allocatePage and "removed" in freePage.
All pages are released (removed) in cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory.
TaskMemoryManager uses the page table when requested to:
Spillable Memory Consumers¶
HashSet<MemoryConsumer> consumers
TaskMemoryManager tracks spillable memory consumers.
TaskMemoryManager registers a new memory consumer when requested to acquire execution memory.
TaskMemoryManager removes (clears) all registered memory consumers when cleaning up all the allocated memory.
Memory consumers are used to report memory usage when TaskMemoryManager is requested to show memory usage.
Memory Acquired But Not Used¶
TaskMemoryManager tracks the size of memory allocated but not used (by any of the MemoryConsumers due to a OutOfMemoryError upon trying to use it).
TaskMemoryManager releases the memory when cleaning up all the allocated memory.
Allocated Pages¶
BitSet allocatedPages
TaskMemoryManager uses a BitSet (Java) to track allocated pages.
The size is exactly the number of entries in the page table (8192).
MemoryMode¶
TaskMemoryManager can be in ON_HEAP or OFF_HEAP mode (to avoid extra work for off-heap and hoping that the JIT handles branching well).
TaskMemoryManager is given the MemoryMode matching the MemoryMode (of the given MemoryManager) when created.
TaskMemoryManager uses the MemoryMode to match to for the following:
For OFF_HEAP mode, TaskMemoryManager has to change offset while encodePageNumberAndOffset and getOffsetInPage.
For OFF_HEAP mode, TaskMemoryManager returns no page.
The MemoryMode is used when:
ShuffleExternalSorteris createdBytesToBytesMapis createdUnsafeExternalSorteris createdSpillableis requested to spill (only when inON_HEAPmode)
Acquiring Execution Memory¶
long acquireExecutionMemory(
long required,
MemoryConsumer consumer)
acquireExecutionMemory allocates up to required execution memory (bytes) for the MemoryConsumer (from the MemoryManager).
When not enough memory could be allocated initially, acquireExecutionMemory requests every consumer (with the same MemoryMode, itself including) to spill.
acquireExecutionMemory returns the amount of memory allocated.
acquireExecutionMemory is used when:
MemoryConsumeris requested to acquire execution memoryTaskMemoryManageris requested to allocate a page
acquireExecutionMemory requests the MemoryManager to acquire execution memory (with required bytes, the taskAttemptId and the MemoryMode of the MemoryConsumer).
In the end, acquireExecutionMemory registers the MemoryConsumer (and adds it to the consumers registry) and prints out the following DEBUG message to the logs:
Task [taskAttemptId] acquired [got] for [consumer]
In case MemoryManager will have offerred less memory than required, acquireExecutionMemory finds the MemoryConsumers (in the consumers registry) with the MemoryMode and non-zero memory used, sorts them by memory usage, requests them (one by one) to spill until enough memory is acquired or there are no more consumers to release memory from (by spilling).
When a MemoryConsumer releases memory, acquireExecutionMemory prints out the following DEBUG message to the logs:
Task [taskAttemptId] released [released] from [c] for [consumer]
In case there is still not enough memory (less than required), acquireExecutionMemory requests the MemoryConsumer (to acquire memory for) to spill.
acquireExecutionMemory prints out the following DEBUG message to the logs:
Task [taskAttemptId] released [released] from itself ([consumer])
Releasing Execution Memory¶
void releaseExecutionMemory(
long size,
MemoryConsumer consumer)
releaseExecutionMemory prints out the following DEBUG message to the logs:
Task [taskAttemptId] release [size] from [consumer]
In the end, releaseExecutionMemory requests the MemoryManager to releaseExecutionMemory.
releaseExecutionMemory is used when:
MemoryConsumeris requested to free up memoryTaskMemoryManageris requested to allocatePage and freePage
Page Size¶
long pageSizeBytes()
pageSizeBytes requests the MemoryManager for the page size.
pageSizeBytes is used when:
Reporting Memory Usage¶
void showMemoryUsage()
showMemoryUsage prints out the following INFO message to the logs (with the taskAttemptId):
Memory used in task [taskAttemptId]
showMemoryUsage requests every MemoryConsumer to report memory used. For consumers with non-zero memory usage, showMemoryUsage prints out the following INFO message to the logs:
Acquired by [consumer]: [memUsage]
showMemoryUsage requests the MemoryManager to getExecutionMemoryUsageForTask to calculate memory not accounted for (that is not associated with a specific consumer).
showMemoryUsage prints out the following INFO messages to the logs:
[memoryNotAccountedFor] bytes of memory were used by task [taskAttemptId] but are not associated with specific consumers
showMemoryUsage requests the MemoryManager for the executionMemoryUsed and storageMemoryUsed and prints out the following INFO message to the logs:
[executionMemoryUsed] bytes of memory are used for execution and
[storageMemoryUsed] bytes of memory are used for storage
showMemoryUsage is used when:
MemoryConsumeris requested to throw an OutOfMemoryError
Cleaning Up All Allocated Memory¶
long cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory()
The consumers collection is then cleared.
cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory finds all the registered MemoryConsumers (in the consumers registry) that still keep some memory used and, for every such consumer, prints out the following DEBUG message to the logs:
unreleased [getUsed] memory from [consumer]
cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory removes all the consumers.
For every MemoryBlock in the pageTable, cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory prints out the following DEBUG message to the logs:
unreleased page: [page] in task [taskAttemptId]
cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory marks the pages to be freed (FREED_IN_TMM_PAGE_NUMBER) and requests the MemoryManager for the tungstenMemoryAllocator to free up the MemoryBlock.
cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory clears the pageTable registry (by assigning null values).
cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory requests the MemoryManager to release execution memory that is not used by any consumer (with the acquiredButNotUsed and the tungstenMemoryMode).
In the end, cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory requests the MemoryManager to release all execution memory for the task.
cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory is used when:
TaskRunneris requested to run a task (and the task has finished successfully)
Allocating Memory Page¶
MemoryBlock allocatePage(
long size,
MemoryConsumer consumer)
allocatePage allocates a block of memory (page) that is:
- Below MAXIMUM_PAGE_SIZE_BYTES maximum size
- For MemoryConsumers with the same MemoryMode as the TaskMemoryManager
allocatePage acquireExecutionMemory (for the size and the MemoryConsumer). allocatePage returns immediately (with null) when this allocation ended up with 0 or less bytes.
allocatePage allocates the first clear bit in the allocatedPages (unless the whole page table is taken and allocatePage throws an IllegalStateException).
allocatePage requests the MemoryManager for the tungstenMemoryAllocator that is requested to allocate the acquired memory.
allocatePage registers the page in the pageTable.
In the end, allocatePage prints out the following TRACE message to the logs and returns the MemoryBlock allocated.
Allocate page number [pageNumber] ([acquired] bytes)
Usage¶
allocatePage is used when:
TooLargePageException¶
For sizes larger than the MAXIMUM_PAGE_SIZE_BYTES allocatePage throws a TooLargePageException.
OutOfMemoryError¶
Requesting the tungstenMemoryAllocator to allocate the acquired memory may throw an OutOfMemoryError. If so, allocatePage prints out the following WARN message to the logs:
Failed to allocate a page ([acquired] bytes), try again.
allocatePage adds the acquired memory to the acquiredButNotUsed and removes the page from the allocatedPages (by clearing the bit).
In the end, allocatePage tries to allocate the page again (recursively).
Releasing Memory Page¶
void freePage(
MemoryBlock page,
MemoryConsumer consumer)
pageSizeBytes requests the MemoryManager for pageSizeBytes.
pageSizeBytes is used when:
Getting Page¶
Object getPage(
long pagePlusOffsetAddress)
getPage handles the ON_HEAP mode of the tungstenMemoryMode only.
getPage looks up the page (by the given address) in the page table and requests it for the base object.
getPage is used when:
ShuffleExternalSorteris requested to writeSortedFileLocation(of BytesToBytesMap) is requested toupdateAddressesAndSizesSortComparator(of UnsafeInMemorySorter) is requested tocomparetwo record pointersSortedIterator(of UnsafeInMemorySorter) is requested toloadNextrecord
getOffsetInPage¶
long getOffsetInPage(
long pagePlusOffsetAddress)
getOffsetInPage gives the offset associated with the given pagePlusOffsetAddress (encoded by encodePageNumberAndOffset).
getOffsetInPage is used when:
ShuffleExternalSorteris requested to writeSortedFileLocation(of BytesToBytesMap) is requested toupdateAddressesAndSizesSortComparator(of UnsafeInMemorySorter) is requested tocomparetwo record pointersSortedIterator(of UnsafeInMemorySorter) is requested toloadNextrecord
Logging¶
Enable ALL logging level for org.apache.spark.memory.TaskMemoryManager logger to see what happens inside.
Add the following line to conf/log4j.properties:
log4j.logger.org.apache.spark.memory.TaskMemoryManager=ALL
Refer to Logging.